Python
Running Python applications through Apache Web Server on AlmaLinux 8 is a popular solution for many system administrators and web developers. By combining the power of Python for back-end processing and the stability of Apache as an HTTP server, we get a reliable and efficient production environment.
This guide will cover step-by-step how to install Python on Apache on an AlmaLinux 8 system, using a mod_wsgi-based approach. We'll outline each part of the process, including installing dependencies, configuring Apache, structuring a Python project, and optimizing your production environment. The guide is detailed and structured for easy follow-through.
Prerequisites
- Full
rootaccess - Apache/HTTPD installed
- Basic Linux Command Line
- Security
Install Python
Before you begin, make sure your system is up to date. Run the command below to update your system:
dnf update -y
dnf install epel-release -y
After that, ensure the Apache HTTP Server (httpd) is installed. If it isn't, please run the following command:
dnf install httpd -y
systemctl enable --now httpd
Allow ports 80 and 443 on firewalld when using it:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}
firewall-cmd --reload
AlmaLinux 8 includes Python 3.x by default. To ensure Python is installed correctly, run the following command:
python3 --version
Here is an example of the output:
Python 3.6.8
If it is not installed, please run the following command to install Python 3:
dnf install python3 python3-pip -y
To run Python applications under Apache, we need the mod_wsgi module. Install using DNF:
dnf install python3-mod_wsgi -y
Then restart Apache:
systemctl restart httpd
Creating a Simple Python Application Structure for Apache
Let's create a simple Python application called myapp. The directories and files will be located in /var/www/myapp.
mkdir -p /var/www/myapp
cd /var/www/myapp
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Create a myapp.wsgi file as an entry point:
nano myapp.wsgi
Fill in the following script:
def application(environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
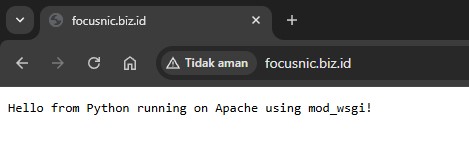
output = b'Hello from Python running on Apache using mod_wsgi!'
response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/plain'),
('Content-Length', str(len(output)))]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return [output]
Adjust permissions:
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/myapp
Now, we need to create a VirtualHost configuration file for the Python application:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id.conf
Fill in the following parameters:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
WSGIDaemonProcess myapp python-home=/var/www/myapp/venv python-path=/var/www/myapp
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/myapp/myapp.wsgi
<Directory /var/www/myapp>
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Then restart Apache:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Open http://YOUR_DOMAIN in a browser to ensure the Python application is running correctly on Apache.
Python Security and Optimization Tips
-
Use a Virtual Environment
Always run Python applications in a virtual environment (virtualenv) to maintain dependency isolation. -
Use a Non-root User
Ensure Apache files and processes are not running as the root user. Use chown to set ownership:
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/myapp
- Performance Optimization
Usemod_wsgiin daemon mode for large-scale applications. You can set the number of processes and threads:
WSGIDaemonProcess myapp processes=5 threads=15
- Logging and Monitoring
Enable error logging and access to facilitate debugging.
Troubleshooting
-
Internal Server Error
Check the Apache log file at/var/log/httpd/$DOMAIN_NAME-error.logto find the cause. The error is usually caused by permissions or typos in the WSGI file. -
Application Not Running Virtualenv
Make sure thepython-homeandpython-pathpaths match thevenvdirectory. -
403 Forbidden
Make sure the/var/www/myappdirectory has read permission for the Apache user.
Conclusion
Combining Apache Web Server and Python on AlmaLinux 8 provides a robust, secure, and production-ready web solution. By following the steps above, we can run WSGI-based Python applications with optimal performance. Proper installation, a clean directory structure, and correct Apache configuration will ensure long-term application stability.
If you're looking for a trusted partner for your AlmaLinux 8-based Python, Django, or Flask server installation needs, don't hesitate to contact Focusnic. We're ready to help you build a fast, secure, and scalable server infrastructure.
Q: Can Python run on Apache without mod_wsgi?
A: Yes, using alternatives like uWSGI + Nginx, but for Apache it is recommended to continue using mod_wsgi.
Q: Should I use a virtual environment?
A: It's highly recommended. This keeps the project modular and doesn't interfere with system-wide Python.
Q: How do I add a Flask or Django application?
A: Frameworks like Flask and Django can be run via WSGI. You just need to adjust the .wsgi file and set the python-path.
Q: How do I turn off a virtual environment?
A: To turn off a Python virtual environment, please run the following command.
deactivate