Security
To improve website security, server configuration extends beyond simply running services. It also involves strengthening the transport layer, HTTP headers, and removing sensitive informatio
n that the web server does not need to display. This article will comprehensively discuss SSL configuration, Hide Server Tokens, basic authentication implementation, and the settings for variou
s HTTP Security Headers such as Strict-Transport-Security, Content-Security-Policy, X-XSS-Protection, X-Frame-Options, and X-Content-Type-Options in Apache Web Server on the AlmaLinux 8
operating system.
Prerequisites
- Full
rootaccess - Basic Linux Command Line
- Security
- Apache/HTTPD is installed
- Domain (optional)
Install Apache
Always perform a system update before installing server applications to ensure compatibility with the latest repositories:
dnf update -y
If you haven't installed Apache, please run the following command:
dnf install httpd -y
systemctl enable --now httpd
Open HTTP and HTTPS ports for Apache:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}
firewall-cmd --reload
Virtualhost
Create a simple virtualhost, which will later be used to implement security hardening:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id.conf
Fill in the following parameters:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Create the following directories and adjust the permissions:
mkdir -p /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
chown apache:apache /var/www/focusnic.biz.id
Create a simple testing file
echo "<h1>Selamat Datang di focusnic.biz.id</h1>" > /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html/index.html
Then restart Apache after making changes to the virtualhost:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Permission
The Apache web server typically runs under the default Apache user account (or another non-privileged account). It's important to ensure that Apache isn't running under a privileged account, such as root. If so, the account should be changed to a non-privileged user to prevent potential security risks.
Verify the current user account under which Apache is running. The expected output should be the user apache running the Apache web server. Run the following command to verify:
[root@localhost ~]# ps -ef | grep httpd
root 18998 1 0 22:05 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 18999 18998 0 22:05 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 19000 18998 0 22:05 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 19001 18998 0 22:05 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 19002 18998 0 22:05 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 19214 18998 0 22:05 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
If Apache is running under the root account or another account with higher privileges, change its configuration to run under a non-privileged account such as apache, nobody, daemon:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Make sure the User and Group parameters are apache:
...
...
..
User apache
Group apache
..
...
...
The apache user must not have sudo privileges:
[root@localhost ~]# sudo -l -U apache
User apache is not allowed to run sudo on localhost.
The apache user must not have access to the login shell:
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd | grep -i apache
apache:x:48:48:Apache:/usr/share/httpd:/sbin/nologin
The password for the apache user must be locked:
[root@localhost ~]# passwd -S apache
apache LK 2025-07-06 -1 -1 -1 -1 (Password locked.)
In addition, SSL files such as private keys and certificates must be changed to root permission and 0600 or 400 mode to prevent SSL leaks.
SSL/TLS
Enabling SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), or more precisely, TLS (Transport Layer Security), on a web server like Apache has the primary function of securing communications between the user (browser) and the server, by encrypting sent and received data.
For Apache to handle HTTPS connections, we first need to install the SSL module:
dnf install mod_ssl -y
Self-Signed SSL
Self-Signed SSL is suitable for development environments or internal servers. Then, follow the instructions that appear:
mkdir /etc/ssl/private
openssl req -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/private.key -out /etc/ssl/private/request.csr
Then generate an SSL certificate for 10 years:
openssl x509 -in /etc/ssl/private/request.csr \
-out /etc/ssl/private/certificate.crt \
-req -signkey /etc/ssl/private/private.key -days 3650
Then add SSL to Virtualhost:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id.conf
Fill in the following parameters:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/private/certificate.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/private.key
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Let's Encrypt SSL
Let's Encrypt provides free, publicly valid certificates. Use Certbot to automate:
dnf install epel-release -y
dnf install certbot python3-certbot-apache -y
Make sure the virtual host remains the default and listens to port 80. Then run the following command to install Let's Encrypt SSL:
certbot --apache -d focusnic.biz.id
Certbot can automatically renew your SSL 30 days before it expires. To test it, please run the following command:
certbot renew --dry-run
Server Tokens
By default, Apache displays information about the server version which can be exploited by irresponsible parties.
Open the Apache main configuration file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Add the following parameters at the very top:
ServerSignature Off
ServerTokens Prod
Add the following parameters at the very top:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Here is the response header before the changes were made:
[root@localhost ~]# curl -I http://localhost
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 18 Jul 2025 17:13:18 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.37 (AlmaLinux) OpenSSL/1.1.1k
Last-Modified: Fri, 11 Jul 2025 14:56:11 GMT
ETag: "2b-639a882be8970"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 43
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Here after making changes to ServerSignature and ServerTokens:
[root@localhost ~]# curl -I http://localhost
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 18 Jul 2025 17:15:45 GMT
Server: Apache
Last-Modified: Fri, 11 Jul 2025 14:56:11 GMT
ETag: "2b-639a882be8970"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 43
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Supported values for the ServerTokens parameter:
ServerTokens Full→ Returns as much information as possible, including version numbers for things like PHP or specific modules. Avoid setting ServerTokens to full!ServerTokens Major→ Place the major version in the server header, for example: Apache/ServerTokens Minor→ Place the major and minor versions in the server header, for example: Apache/2.4ServerTokens MinorServerTokens Minimal→ Returns the full Apache version number in the server header, for example: Apache/2.4.37ServerTokens OS→ Returns the full Apache version number and OS name, for example: Apache/2.4.37 (AlmaLinux) - this is often the default on popular Linux distributions because they want to promote their brand as much as possible.ServerTokens ProdorServerTokens ProductOnly→ It only returns the server product nameApacheand this is the most recommended one to use.
The value for ServerSignature is:
ServerSignature On→ Displays a signature containing the Apache version number.ServerSignature Off→ Does not display the server version at the bottom of error pages or directory listing pages.ServerSignature EMail→ Returns the email address specified in theServerAdmindirective.
HTTP/2
HTTP/2 is the latest version of the HTTP protocol, bringing several performance improvements, including:
- Multiplexing: Sending multiple requests simultaneously without waiting for individual responses.
- Header compression (HPACK): Reducing header delivery overhead.
- Priority and server push: Accelerating page load times.
- Faster and more efficient than HTTP/1.1
HTTP/2 can only be used over HTTPS (SSL) in Apache, so SSL activation is an absolute requirement before enabling HTTP/2.
Apache HTTP/2 requires at least Apache 2.4.17 and mod_http2. AlmaLinux 8 usually includes it by default. Verify the module:
httpd -M | grep http2
Output example:
proxy_http2_module (shared)
Enable HTTP/2 on virtualhost:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Add the Protocols h2 http/1.1 parameter inside the <VirtualHost> line:
IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Then restart Apache after making the changes:
systemctl restart httpd
Verify:
[root@localhost ~]# curl -I --http2 -k https://focusnic.biz.id
HTTP/2 200
date: Sat, 19 Jul 2025 11:09:25 GMT
server: Apache
last-modified: Fri, 11 Jul 2025 14:56:11 GMT
etag: "2b-639a882be8970"
accept-ranges: bytes
content-length: 43
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Verification can also be done through the browser Developer Tools:
- Press F12 → Network Tab
- Add the
Protocolcolumn, you will seeh2for HTTP/2 connections
HTTP Basic Authentication
HTTP Basic Authentication is the simplest and most widely used authentication method for protecting web pages. The mechanism is:
- The client (browser) sends the username and password encoded in Base64 format.
- Apache verifies these credentials from the
.htpasswdfile.
Install httpd-tools to create a password file:
dnf install httpd-tools -y
Create a password and username file for authentication:
htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/.htpasswd focusnic
If you want to add another user, please use the following command without the -c parameter:
htpasswd /etc/.htpasswd focusnic-client
Then adjust the permissions and this file should only be accessible by root:
chmod 640 /etc/httpd/.htpasswd
chown root:apache /etc/httpd/.htpasswd
Add the following parameters in virtualhost:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Add the following parameters:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
<Directory "/var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html">
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Restricted Content"
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/.htpasswd
Require valid-user
</Directory>
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Or you can also use .htaccess
nano /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html/.htaccess
Fill in the following parameters:
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Admin Area"
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/.htpasswd
Require valid-user
Then restart Apache:
systemctl restart httpd
Then access via browser http://$DOMAIN
You can also use curl:
curl -u namauser:password https://focusnic.biz.id
Whitelist IP Address
To whitelist an IP address in Apache Web Server on AlmaLinux 8, you can use the Require ip directive within the <Directory>, <Location> blocks, or directly within the Virtual Host configuration. This method is very effective for restricting access from specific IP addresses, either for the entire site or just a specific directory, such as /admin.
Whitelist IP addresses for all paths in the virtual host:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Fill in the following parameters
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
<Directory /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html>
Require all denied
Require ip 192.168.2.4
Require ip 192.168.1.20
</Directory>
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Whitelist for specific directories:
<Directory /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html/wp-admin>
Require all denied
Require ip 192.168.2.4
Require ip 192.168.1.20
</Directory>
Whitelist IP Using .htaccess:
nano /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html/.htaccess
Fill in the following parameters:
Require all denied
Require ip 192.168.2.4
Require ip 192.168.1.20
Then restart Apache:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
To test, please access the domain via a browser. If the response is 403 (Forbidden), the IP whitelist has been successful.
Security Headers
Security Headers in Apache Web Server, which are crucial for strengthening the security of your web applications and protecting against various types of attacks such as XSS, clickjacking, and MIME sniffing. Here is a complete list of Apache Security Headers:
| Security Header | Main Function | Configuration Example in Apache |
|---|---|---|
| Strict-Transport-Security | Forces the browser to use only HTTPS, preventing downgrade to HTTP. | Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" |
| Content-Security-Policy | Prevent XSS by setting the resources (scripts, styles, images, etc.) that are allowed to run. | Header set Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://apis.google.com" |
| X-XSS-Protection | Enables XSS filtering on modern browsers. (Legacy, now not recommended on modern browsers) | Header set X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" |
| X-Frame-Options | Prevent websites from being opened inside iframes (anti clickjacking). | Header set X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" |
| X-Content-Type-Options | Prevents MIME sniffing, only allowing content types as declared. | Header set X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" |
| Referrer-Policy | Control referrer data sent to other sites to maintain privacy. | Header set Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" |
Permissions-Policy (formerly: Feature-Policy) | Control access to browser features such as camera, microphone, geolocation etc. from web pages. | Header set Permissions-Policy "geolocation=(), microphone=(), camera=()" |
| Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy (COEP) | Protecting resources from loading third-party content without explicit permission (related to web resource isolation). | Header set Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy "require-corp" |
| Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy (COOP) | Ensures pages have separate browsing contexts (for process isolation security). | Header set Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy "same-origin" |
| Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy (CORP) | Determine who can access resources such as images, fonts, etc. from other domains. | Header set Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy "same-origin" |
Before configuring headers, make sure the mod_headers module is active:
httpd -M | grep headers
Output example:
headers_module (shared)
Then configure all the headers in the table above on the following virtual host:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Add the following parameters:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload"
Header set Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; object-src 'none'"
Header set X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block"
Header set X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN"
Header set X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff"
Header set Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade"
Header set Permissions-Policy "geolocation=(), microphone=(), camera=()"
Header set Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy "require-corp"
Header set Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy "same-origin"
Header set Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy "same-origin"
</IfModule>
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Then restart Apache:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Then test on the following site to check the security headers https://securityheaders.com/
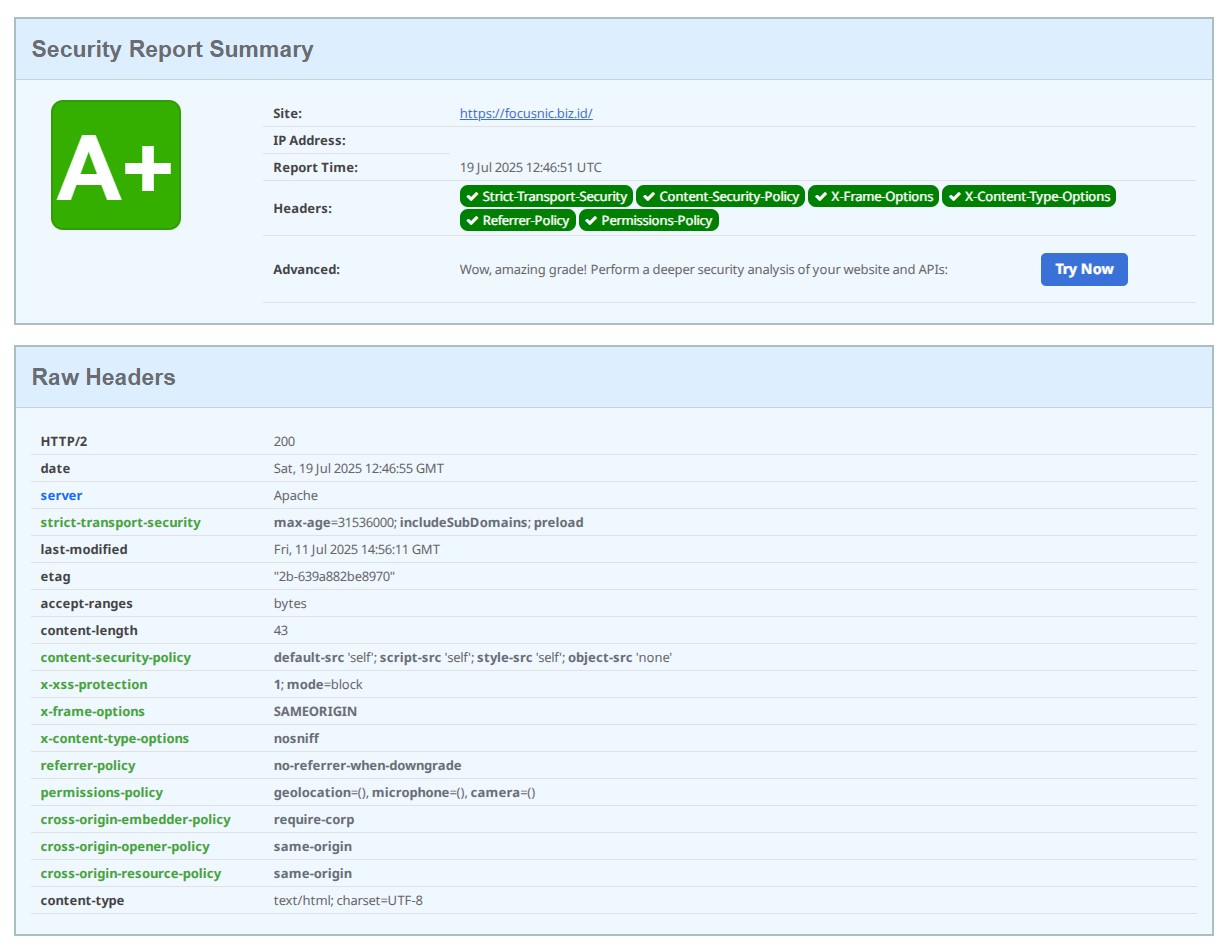
Verify using curl:
[root@localhost ~]# curl -I https://focusnic.biz.id
HTTP/2 200
date: Sat, 19 Jul 2025 12:50:15 GMT
server: Apache
strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload
last-modified: Fri, 11 Jul 2025 14:56:11 GMT
etag: "2b-639a882be8970"
accept-ranges: bytes
content-length: 43
content-security-policy: default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; object-src 'none'
x-xss-protection: 1; mode=block
x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN
x-content-type-options: nosniff
referrer-policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
permissions-policy: geolocation=(), microphone=(), camera=()
cross-origin-embedder-policy: require-corp
cross-origin-opener-policy: same-origin
cross-origin-resource-policy: same-origin
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Minimum Recommendations for Production Sites
For a typical website, here are the most secure and commonly used configurations:
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubDomains; preload"
Header set X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff"
Header set X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN"
Header set X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block"
Header set Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade"
Header set Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'"
Options
Apache uses the Options directive in the Directory, VirtualHost, or .htaccess configuration to control how files and directories are accessed and executed.
| Parameters | Description | Security Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
All | Enables all options except MultiViews. Equivalent to Indexes FollowSymLinks Includes ExecCGI. | Not recommended as it is too permissive. Use the specific options as needed. |
None | Disables all additional features in the directory. | Safest. Use if you don't need additional features. |
Indexes | Menampilkan listing isi direktori jika tidak ada file default (misalnya index.html). | Nonaktifkan jika tidak ingin pengunjung melihat struktur file (Options -Indexes). |
Includes | Allows the use of Server Side Includes (SSI) in .shtml files. | Use with caution, as SSI can be used to execute system commands. |
IncludesNOEXEC | Same as Includes but without the ability to execute external scripts or commands. | Safer than Includes, use if you only need to include static files. |
FollowSymLinks | Allows Apache to follow symbolic links. | Use with SymLinksIfOwnerMatch for security. |
SymLinksIfOwnerMatch | Apache only follows symbolic links if the owner of the link and the target file are the same. | More secure than regular FollowSymLinks. Recommended for shared hosting. |
ExecCGI | Enables execution of CGI files (.cgi, .pl, .py, etc.). | Only enable in specific, tightly controlled directories. |
MultiViews | Enables content negotiation, allowing Apache to select files based on browser preferences (such as index.en.html, index.fr.html). | Use if multilingual is supported. Not harmful, but can cause confusion. |
RunScripts | (Aka ExecCGI) Typically used in older configurations. | Uncommon, use ExecCGI directly. |
In a production environment, it is not recommended to enable all Options options, as some may be security holes or cause unnecessary overhead.
| Parameters | Commonly Used? | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
FollowSymLinks | ❌ No | If a symbolic link points to a file or folder outside the document root (for example, to a critical system or configuration file), it can potentially open up uncontrolled access to sensitive resources. |
-Indexes | ✅ Highly Recommended | Disables directory listing. It is important to keep files/folders invisible. |
None | ✅ Yes | Disables all options, used for maximum security. |
IncludesNOEXEC | ⚠️ Sometimes | Allow server-side includes without script execution capabilities (safer). |
ExecCGI | ❌ Rare | Only used if you absolutely need to run CGI. Best avoided. |
MultiViews | ❌ Rare | Used for content negotiation. Rarely needed in a standard setup. |
SymLinksIfOwnerMatch | ✅ Safe Alternative | Like FollowSymLinks, but only if the file owner is the same (safer). |
Here is an example of a virtual host:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Fill in the following parameters:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
<Directory "/var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html">
Options -Indexes -FollowSymLinks -ExecCGI
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Then restart Apache:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
UserDir
Apache's UserDir feature is a module that allows system users (user accounts on Linux systems) to serve their web files through username-based URLs. An example of accessing a website with UserDir enabled is: http://example.com/~example. By default, Apache will map this URL to: /home/username/public_html/.
In production environments, the use of **UserDir** in Apache is very rarely recommended, and is often disabled by default, for the following reasons:
- High Security Risk: Any user on the system can serve web content** through
~/public_html, and this opens up opportunities for configuration errors, such as:
- Private files that should not be public.
- Uncontrolled use of
htaccess. - Potential upload of malicious files to the
public_htmlfolder.
- Not Compliant with Modern Deployment Standards:
- Modern platforms like Laravel, Django, WordPress, and Node.js do not rely on the
UserDirstructure. - Production websites typically have a dedicated directory structure in
/var/www/or/opt/web/, not the user's home directory.
- Difficult to Manage and Audit. The large number of active
~/public_htmlfolders makes it difficult to:
- Security audits.
- Central logging.
- File and permissions management.
To block UserDir access please add the following LocationMatch parameter to the virtualhost:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Fill in the following parameters:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
<LocationMatch "^/~">
Require all denied
</LocationMatch>
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
If you don't use it at all, you can disable the module:
rm -f /etc/httpd/conf.d/userdir.conf
Then restart Apache:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
HTTP Method
To improve the security of Apache Web Server in a production environment, we recommend disabling unnecessary HTTP methods.
| HTTP Methods | Commonly Used? | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | ✅ Yes | To get data from the server |
| POST | ✅ Yes | To send data to the server (form, API) |
| HEAD | ✅ Yes | Same as GET but header only |
| OPTIONS | ⚠️ Sometimes | Used for CORS preflight, should be limited |
| PUT | ❌ No | To replace/upload resources, rarely used on general websites |
| DELETE | ❌ No | Deletes resources; prone to abuse |
| TRACE | ❌ No | For debugging, often used for exploitation (XST) |
| CONNECT | ❌ No | For proxy tunneling (usually HTTPS); no need to enable in Apache |
Production Recommendations:
- Allow only: GET, POST, HEAD
- Deny all other methods
- Use a layer 7 firewall (mod_security, CDN, or WAF) for further validation
How to check the HTTP Methods enabled on the server, focus on the allow parameter:
[root@localhost ~]# curl -i -k -X OPTIONS https://focusnic.biz.id
HTTP/2 200
date: Sat, 19 Jul 2025 14:47:51 GMT
server: Apache
allow: GET,POST,OPTIONS,HEAD,TRACE
content-length: 0
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Disable HTTP method TRACE on all virtualhosts (global):
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Fill in the following parameters at the very top of the configuration:
TraceEnable Off
Then limit GET, POST, and HEAD on the virtualhost:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Add the LimitExcept parameter:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
<Directory /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html>
Options -Indexes
AllowOverride All
<LimitExcept GET POST HEAD>
Require all denied
</LimitExcept>
</Directory>
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Benefits:
| Effects | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Increased security | Closes the door to high-risk methods such as PUT, DELETE, and TRACE, which are often used in exploits. |
| Protection against XST and HTTP Verb Tunneling attacks | For example, an attack using TRACE to steal cookies via cross-site tracing. |
| Reduce the attack surface | Limit interactions to only the methods the application actually needs. |
| Compliance with security standards | Compliant with OWASP recommendations and server security audits. |
Things to Watch Out For:
| Potential Problems | Explanation |
|---|---|
| If your app requires other methods, it may break | For example, RESTful APIs sometimes require PUT or DELETE. You need to open access to them specifically for specific endpoints. |
| OPTIONS for CORS preflight will be blocked | If your site has CORS enabled and OPTIONS is blocked, errors may occur with cross-domain requests. |
Verify:
curl -X DELETE https://focusnic.biz.id
curl -X TRACE https://focusnic.biz.id
curl -v -X OPTIONS https://focusnic.biz.id
Block Dotfiles
To block access to sensitive files in Apache Web Server, we can use a combination of the <Files>, <FilesMatch> directives, and access controls such as Require all denied to prevent certain files from being accessed via URL, even if they are physically located in the DocumentRoot. This is a crucial part of hardening web servers in production environments.
| File Types | Examples | Blocking Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration files | .env, .htaccess, config.php | Stores credentials/database/config |
| Backup files | db.sql, site.zip, .tar.gz | Can be downloaded and abused |
| Dotfiles | .git, .env, .bashrc | Internal information that should not be exposed |
| Source code | .phps, .bak, .old, .swp | Can leak application structure |
Add the following parameters to block dotfiles and other sensitive files on <VirtualHost>:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id.conf
Add the following parameters:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
<FilesMatch "\.(env|git|htaccess|log|bak|old|sql|tar\.gz|zip|swp|phps)$">
Require all denied
</FilesMatch>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>