Tuning
Apache HTTP Server, or Apache, is one of the most popular web servers used in Linux-based server environments, including AlmaLinux 8. This Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)-based operating system is well-suited for web server needs due to its stability, high security, and extensive community support. However, for Apache to run efficiently and optimally, it requires proper tuning and configuration according to the workload, memory, and number of users.
This guide will cover in-depth and comprehensive information on how to optimally tune and configure Apache on AlmaLinux 8, including module settings, workers, connections, caching, and security.
Prerequisites
- Full
rootaccess - Apache/HTTPD installed
- Basic Linux Command Line
Preparation
Before tuning Apache, ensure your system is running AlmaLinux 8 and that Apache is installed. To install Apache, use the following command:
dnf update -y
dnf install httpd httpd-tools -y
systemctl enable httpd --now
Then open ports 80 and 443, if using firewalld run the following command:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}
firewall-cmd --reload
MPM (Multi-Processing Module)
If you are using modern PHP, avoid mod_php and use PHP-FPM to take advantage of MPM workers or events.
MPM (Multi-Processing Module) is the main component of Apache that regulates how Apache handles requests from clients, especially in terms of:
- Processes and threads used
- Load distribution across CPU and RAM
- Concurrent connection capacity
Each Apache server can only run one MPM at a time, and the choice of MPM significantly impacts performance, resource consumption, and compatibility with other modules, such as PHP. Apache provides three main MPMs in common use:
- Prefork MPM – a pure, threadless process, stable but resource-intensive.
- Worker MPM – a threaded process, more efficient and suitable for modern applications.
- Event MPM – an extension of Worker, more efficient for keep-alive connections and HTTP/2.
| Features / Characteristics | MPM Prefork | MPM Worker | MPM Event |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution Model | Single process per connection | Multi-threaded process | Multi-threaded process & event loop |
| Threading | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Performance | Slow & memory-hungry | Faster & more efficient | Most efficient for keep-alive connections |
| Memory Usage | High | Medium | Lowest |
| mod_php compatibility | ✅ Compatible | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| HTTP/2 Support | ❌ Not optimal | ❌ Not optimal | ✅ Yes |
| Ideal For | Legacy applications, mod_php, stable | PHP-FPM, modern applications | PHP-FPM, high traffic, HTTP/2 |
| Response to KeepAlive | Blocking | Blocking | Non-blocking |
| Recommended Production? | ⚠️ Legacy/Limited | ✅ For modern servers | ✅✅ Most recommended |
Here's what you need to do if you want to adapt to your current application needs:
| Requirements | Select MPM |
|---|---|
Running legacy mod_php | Prefork |
Using PHP-FPM, a modern application | Worker |
| Websites with many keep-alive connections / HTTP/2 | Event |
| Minimize RAM usage | Event |
| Static websites or lightweight APIs | Worker / Event |
Event
Optimization of the number of Workers and Threads is server-wide, not per VirtualHost.
To use the mpm_event_module module please edit the following file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.conf
Then add the mpm_event_module parameter and comment out or delete the other mpm_ lines:
Optimization on the server assuming specifications of 4GB RAM and 2 CPU.
LoadModule mpm_event_module modules/mod_mpm_event.so
#LoadModule mpm_worker_module modules/mod_mpm_worker.so
#LoadModule mpm_prefork_module modules/mod_mpm_prefork.so
<IfModule mpm_event_module>
StartServers 2
MinSpareThreads 25
MaxSpareThreads 75
ThreadsPerChild 25
MaxRequestWorkers 150
MaxConnectionsPerChild 3000
</IfModule>
The following is an explanation of the parameters above:
| Directive | Function | Suggested Value | Reason for Selecting Value | Formula / Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
StartServers | Number of Apache child processes to run at startup | 2 | Sufficient for a small server (2 vCPUs), starting with 50 threads (2 × 25) ready to serve connections | StartServers × ThreadsPerChild = 2 × 25 = 50 threads |
MinSpareThreads | Minimum number of idle threads before Apache creates new threads | 25 | Maintains performance so Apache doesn't run out of threads when demand spikes suddenly | — |
MaxSpareThreads | Maximum number of idle threads before Apache kills excess threads | 75 | Prevents memory overcommitment when load decreases, while maintaining thread availability | — |
ThreadsPerChild | Number of threads per Apache child process | 25 | Ideal number to maintain stable load distribution and easy control | MaxRequestWorkers ÷ ThreadsPerChild = number of children |
MaxRequestWorkers | Maximum number of active connections served by Apache simultaneously | 150 | Adjusted to RAM (4GB) and light-medium load targets without causing the server to run out of memory | 25 × 6 = 150 (6 child processes) |
MaxConnectionsPerChild | Number of connections handled per process before the process is restarted | 3000 | Prevents long-term memory leaks without restarting the process too often | — |
Additionally, the MaxRequestWorkers parameter can be optimized and adjusted to suit current Apache load conditions. Follow these steps:
- Check Apache processes with the following command to see which processes on Apache are using RAM (in MB):
ps -ylC httpd --sort:rss | awk 'NR!=1 {print $8 / 1024}'
- Estimate with the value that appears most often.
- Run the following command to see the available RAM (in MB):
free -m | awk 'NR==2 {print $7}'
- Then apply the formula (Available Memory/Apache Process). For example, if each process has 15 MB and total RAM is 4 GB, the usable value for
MaxRequestWorkersis 230. Make sure to always leave some RAM for the system.
Save Apache changes by restarting it:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Verify:
httpd -V | grep -i mpm
httpd -M | grep mpm
Output example:
Server MPM: event
mpm_event_module (shared)
Worker
Optimization of the number of Workers and Threads is server-wide, not per VirtualHost.
To use the mpm_worker_module module please edit the following file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.conf
Then add the mpm_worker_module parameter and comment out or delete the other mpm_ lines:
Optimization on the server assuming specifications of 4GB RAM and 2 CPU.
#LoadModule mpm_event_module modules/mod_mpm_event.so
LoadModule mpm_worker_module modules/mod_mpm_worker.so
#LoadModule mpm_prefork_module modules/mod_mpm_prefork.so
<IfModule mpm_worker_module>
StartServers 2
MinSpareThreads 25
MaxSpareThreads 75
ThreadLimit 64
ThreadsPerChild 25
MaxRequestWorkers 150
MaxConnectionsPerChild 3000
</IfModule>
The following is an explanation of the parameters above:
| Directive | Function | Value | Reason for Selecting Value | Formula / Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
StartServers | Number of child processes to run when Apache starts | 2 | Provides 2 × 25 = 50 threads ready to serve from the start. Suitable for 2 vCPUs, lightweight & responsive | StartServers × ThreadsPerChild = 2 × 25 = 50 threads |
MinSpareThreads | Minimum number of idle threads available before Apache creates new ones | 25 | Maintains performance by preventing threads from running out during sudden requests | — |
MaxSpareThreads | Maximum idle threads before Apache kills excess threads | 75 | Prevents excessive RAM consumption from idle threads | — |
ThreadLimit | Maximum limit of ThreadsPerChild value that can be set | 64 | Adjusted for flexible scaling; must be ≥ ThreadsPerChild | ThreadLimit ≥ThreadsPerChild |
ThreadsPerChild | Number of threads created per child process | 25 | Small enough to be memory efficient per child & easy to manage, ideal for 2 vCPUs | MaxRequestWorkers ÷ ThreadsPerChild = 6 processes |
MaxRequestWorkers | Maximum number of simultaneous connections Apache can handle | 150 | Active connection load limit. Adjusted to stay light on 4GB RAM (estimated 150 × 20 MB = ±3GB RAM) | ThreadsPerChild × Child = MaxRequestWorkers → 25 × 6 = 150 |
MaxConnectionsPerChild | Maximum number of connections that can be processed before the child is restarted | 3000 | Prevents memory leaks. 3000 = compromise between performance & long-term process stability | Estimation: 3000 requests × 0.2 seconds/request = ±10 minutes process uptime |
Additionally, the MaxRequestWorkers parameter can be optimized and adjusted to suit current Apache load conditions. Follow these steps:
- Check the Apache process with the following command to see the processes on Apache that are using RAM (in MB):
ps -ylC httpd --sort:rss | awk 'NR!=1 {print $8 / 1024}'
- Estimate using the most frequently occurring value.
- Run the following command to view the available RAM (in MB):
free -m | awk 'NR==2 {print $7}'
- Then apply the formula (Available Memory/Apache Process). For example, if each process has 15 MB and total RAM is 4 GB, the usable value for
MaxRequestWorkersis 230. Make sure to always leave some RAM for the system.
Save Apache changes by restarting it:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Verify:
httpd -V | grep -i mpm
httpd -M | grep mpm
Output example:
Server MPM: worker
mpm_worker_module (shared)
Prefork
Optimization of the number of Workers and Threads is server-wide, not per VirtualHost.
To use the mpm_worker_module module please edit the following file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.conf
Then add the mpm_prefork_module parameter and comment out or delete the other mpm_ lines:
Optimization on the server assuming specifications of 4GB RAM and 2 CPU.
#LoadModule mpm_event_module modules/mod_mpm_event.so
#LoadModule mpm_worker_module modules/mod_mpm_worker.so
LoadModule mpm_prefork_module modules/mod_mpm_prefork.so
<IfModule mpm_prefork_module>
StartServers 3
MinSpareServers 3
MaxSpareServers 5
MaxRequestWorkers 50
MaxConnectionsPerChild 300
</IfModule>
The following is an explanation of the parameters above:
| Directive | Function | Value | Reason for Selecting Value | Formula / Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
StartServers | Number of Apache processes to start immediately | 3 | Provides 3 processes ready to serve connections. Sufficient for light to moderate initial server loads | — |
MinSpareServers | Minimum number of idle processes. If there are fewer, Apache will create new processes | 3 | Keep Apache from running out of idle processes during light traffic spikes | — |
MaxSpareServers | Maximum number of idle processes. If there are more, Apache will kill the excess. | 5 | Save memory when the server is idle with low load. | — |
MaxRequestWorkers | Maximum number of simultaneous connections that can be served | 50 | Suitable for servers with 4GB RAM and mod_php. Each process can consume 30–50MB of RAM | 50 × 40MB ≈ 2 GB RAM |
MaxConnectionsPerChild | Maximum number of connections a process can handle before it is restarted | 300 | Avoids memory leaks. Processes will be rotated after serving 300 requests | Estimate: 300 × 0.2 seconds/request = ±1 minute uptime per process |
Additionally, the MaxRequestWorkers parameter can be optimized and adjusted to suit current Apache load conditions. Follow these steps:
- Check the Apache process with the following command to see the processes on Apache that are using RAM (in MB):
ps -ylC httpd --sort:rss | awk 'NR!=1 {print $8 / 1024}'
- Estimate using the most frequently occurring value.
- Run the following command to view the available RAM (in MB):
free -m | awk 'NR==2 {print $7}'
- Then apply the formula (Available Memory/Apache Process). For example, if each process has 15 MB and total RAM is 4 GB, the usable value for
MaxRequestWorkersis 230. Make sure to always leave enough RAM for the system.
Save your changes by restarting Apache:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Verify:
httpd -V | grep -i mpm
httpd -M | grep mpm
Output example:
Server MPM: prefork
mpm_prefork_module (shared)
KeepAlive
This configuration applies to the entire Apache server or virtual host (server-wide), cannot be customized per VirtualHost, and will affect all incoming HTTP connections to that server.
KeepAlive allows connections to remain open and speeds up loading for subsequent requests. The timeout should be adjusted to avoid overloading the server. Please edit the following file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Change the following section or place it at the beginning of the global section, before the <VirtualHost> configuration:
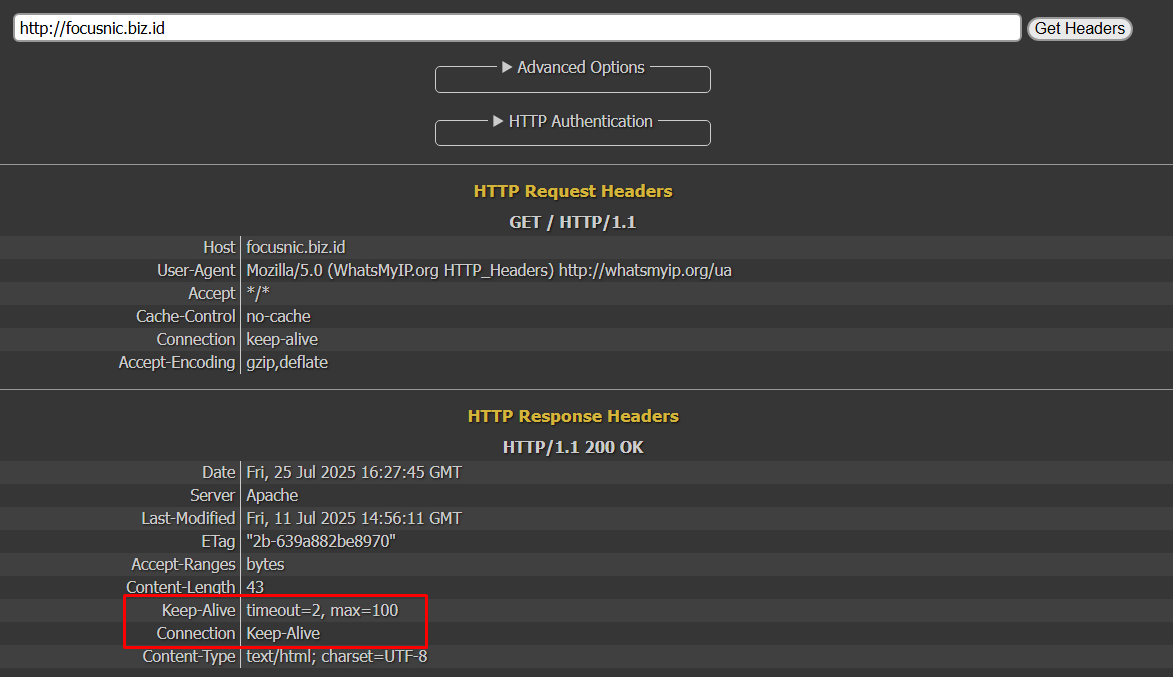
KeepAlive On
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
KeepAliveTimeout 2
Explanation:
KeepAlive On→ Client (browser) can send multiple HTTP requests over a single TCP connection. Reduces TCP handshake overhead, speeding up loading of pages containing many files (images, CSS, JS).MaxKeepAliveRequests 100→ Specifies the maximum number of HTTP requests that can be sent over a singleKeepAliveconnection before the connection is closed.KeepAliveTimeout 2→ Specifies how many seconds the server will wait for the next request before closing an idleKeepAliveconnection, if there is no further request within 2 seconds, Apache will close the connection. On a production server, the longer the timeout, the more workers or threads will be idle just waiting for requests that may not come.
| Directive | Function | Value | Reason for Selection |
|---|---|---|---|
KeepAlive | Enables persistent HTTP connections | On | Improves HTTP connection efficiency, speeding up modern page loads |
MaxKeepAliveRequests | Limits the number of requests per TCP connection before closing | 100 | Sufficient for complex pages, prevents connections from staying idle for too long |
KeepAliveTimeout | Wait time (in seconds) if the connection is idle waiting for the next request | 2 | Avoids wasting threads, speeds up worker slot release |
Then restart Apache to save the changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
To verify the configuration, you can use the following website https://www.whatsmyip.org/http-headers/
Caching
Caching is key to improving website speed. Apache has four commonly used modules: mod_cache, mod_cache_disk, mod_expires, and mod_deflate.
| Module | Main Functions | Recommended in Production? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
mod_cache | The main caching framework, acts as a controller for the cache backend | ✅ Yes | Used in conjunction with mod_cache_disk or mod_cache_socache |
mod_cache_disk | Stores cache to file/disk | ✅ Yes | Suitable for caching static files, HTML, images, etc. Ideal for sites with a lot of static content |
mod_cache_socache | Stores cache in Shared Object Cache (memory, like shmcb) | ⚠️ Depends | Faster than disk, but limited in size and requires tuning of other mod_socache_* |
mod_file_cache | Preload static files into memory when Apache starts (e.g. favicon, logo) | ⚠️ Optional | Useful if small files are accessed very frequently. Should be used with caution due to RAM consumption |
mod_mem_cache | Legacy, replaced by mod_cache_socache | ❌ No | Not recommended for modern Apache (2.4.x and above) |
mod_expires | Sets HTTP caching headers (Expires and Cache-Control) | ✅ Highly recommended | Works at the header level, not cache. Very effective for browser cache control |
mod_headers | Used to modify or add HTTP headers, including caching headers | ✅ Highly recommended | Can be used with mod_expires for complex headers |
mod_deflate | Compress HTTP output (HTML, CSS, JS, JSON, XML) with Gzip | ✅ Yes | Reduce response size, increase page load speed |
Server Cache
The following configuration will be done per virtualhost not server-wide.
The cache server will implement a disk-based storage model and use the cache_disk_module and cache_module modules. Ensure the modules are enabled:
httpd -M | grep cache
Output example:
cache_module (shared)
cache_disk_module (shared)
If it is not activated, please load the module in the following file.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-base.conf
Add the following parameters:
LoadModule cache_module modules/mod_cache.so
LoadModule cache_disk_module modules/mod_cache_disk.so
Then restart Apache to save the changes and check the results again:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Then create a CacheRoot on server-wide which functions to store the cache location so as not to redefine it on each virtualhost:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Add the following parameters at the very end of the file:
<IfModule mod_cache.c>
CacheRoot "/var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk"
CacheDirLevels 2
CacheDirLength 1
</IfModule>
Then create a CacheRoot directory and adjust the permissions:
mkdir -p /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk
chown apache:apache -R /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk
Then create a virtualhost or adjust the following parameters:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id.conf
Add the following parameters to enable caching on the public_html and also style directories:
Please adjust the location or path you want to cache by changing the CacheEnable disk / parameter, for example to CacheEnable disk /css and so on.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
<IfModule mod_cache.c>
CacheEnable disk /
CacheEnable disk /style
CacheHeader on
CacheDefaultExpire 10
CacheMaxExpire 86400
CacheIgnoreNoLastMod On
</IfModule>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Restart Apache to save changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Please verify by accessing it via browser console or via CURL, then make sure the response is X-Cache: HIT:
[root@localhost ~]# curl -I http://focusnic.biz.id/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Sat, 26 Jul 2025 08:50:41 GMT
Server: Apache
Last-Modified: Fri, 11 Jul 2025 14:56:11 GMT
ETag: "2b-639a882be8970"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 43
Age: 360
X-Cache: HIT from focusnic.biz.id
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
[root@localhost ~]# curl -I http://focusnic.biz.id/uploads/info.php
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Sat, 26 Jul 2025 08:47:33 GMT
Server: Apache
X-Powered-By: PHP/8.4.10
Age: 14
X-Cache: HIT from focusnic.biz.id
Content-Length: 81770
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Then check on the server side:
ls -lah /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk/*/*
Output example:
/var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk/M/z:
total 84K
drwx------. 2 apache apache 74 Jul 26 15:47 .
drwx------. 3 apache apache 15 Jul 26 15:47 ..
-rw-------. 1 apache apache 80K Jul 26 15:47 ykCo0j02gjUwGjHFkReg.data
-rw-------. 1 apache apache 738 Jul 26 15:47 ykCo0j02gjUwGjHFkReg.header
/var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk/W/D:
total 8.0K
drwx------. 2 apache apache 74 Jul 26 15:44 .
drwx------. 3 apache apache 15 Jul 26 15:44 ..
-rw-------. 1 apache apache 43 Jul 26 15:44 KERT3etnTDHHgli7T9Tg.data
-rw-------. 1 apache apache 810 Jul 26 15:44 KERT3etnTDHHgli7T9Tg.header
Check using the htcacheclean command:
htcacheclean -A -v -p /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk
Output example:
http://focusnic.biz.id:80/? 810 43 200 0 1753519481246968 1753605881246968 1753519481246634 1753519481246968 1 0
http://focusnic.biz.id:80/uploads/info.php? 738 81770 200 0 1753519639081579 1753520239081579 1753519639079998 1753519639081579 1 0
Clear the cache using the htcacheclean command:
htcacheclean -l 1k -v -t -p /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk/
Output example:
Cleaned /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk. Statistics:
size limit 1.0K
inodes limit 0
total size was 81.8K, total size now 0.4K
total inodes was 12, total inodes now 4
total entries was 3, total entries now 1
2 entries deleted (0 from future, 0 expired, 2 fresh)
Automate cache clearing every minute using htcacheclean with daemonize mode:
htcacheclean -d 1m -l 1k -t -p /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk/
Check the daemon htcacheclean process:
ps aux |grep htcache
Output example:
root 3540 0.0 0.0 19824 176 ? Ss 15:56 0:00 htcacheclean -d 1m -l 1k -t -p /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk/
Browser Cache
Another interesting and widely used Apache tuning is enabling browser caching (HTTP cache) using mod_expires and mod_headers, which is the most common and efficient method for improving website performance.
Make sure the module is active, check using the following command:
httpd -M | grep expires
httpd -M | grep headers
Example of expected output:
expires_module (shared)
headers_module (shared)
If it doesn't appear, please activate it in the following file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-base.conf
Then fill in or add the following parameters:
LoadModule expires_module modules/mod_expires.so
LoadModule headers_module modules/mod_headers.so
Restart Apache to save the changes and check the module again:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
The following server-wide cache configuration means all virtualhosts will be affected:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Add the following parameters at the very end of the file:
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive On
# Default for all files
ExpiresDefault "access plus 1 day"
# Caching for MIME
ExpiresByType image/jpg "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/gif "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/png "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/webp "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/svg+xml "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/css "access plus 7 days"
ExpiresByType text/javascript "access plus 7 days"
ExpiresByType application/javascript "access plus 7 days"
ExpiresByType text/html "access plus 1 hour"
ExpiresByType application/json "access plus 1 hour"
ExpiresByType application/xml "access plus 1 hour"
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
# Control cache for static files
<FilesMatch "\.(ico|jpg|jpeg|png|gif|webp|svg|css|js)$">
Header set Cache-Control "public, max-age=2592000, immutable"
</FilesMatch>
# Disable cache for dynamic files
<FilesMatch "\.(php|html|htm)$">
Header set Cache-Control "no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate"
Header set Pragma "no-cache"
Header set Expires 0
</FilesMatch>
</IfModule>
For per virtual host or individual per website/domain, please add the following parameters:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive On
# Default for all files
ExpiresDefault "access plus 1 day"
# Caching for MIME
ExpiresByType image/jpg "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/gif "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/png "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/webp "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType image/svg+xml "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/css "access plus 7 days"
ExpiresByType text/javascript "access plus 7 days"
ExpiresByType application/javascript "access plus 7 days"
ExpiresByType text/html "access plus 1 hour"
ExpiresByType application/json "access plus 1 hour"
ExpiresByType application/xml "access plus 1 hour"
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
# Control cache for static files
<FilesMatch "\.(ico|jpg|jpeg|png|gif|webp|svg|css|js)$">
Header set Cache-Control "public, max-age=2592000, immutable"
</FilesMatch>
# Disable cache for dynamic files
<FilesMatch "\.(php|html|htm)$">
Header set Cache-Control "no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate"
Header set Pragma "no-cache"
Header set Expires 0
</FilesMatch>
</IfModule>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Parameter explanation:
| File Type | Cache Duration | Destination |
|---|---|---|
Image (jpg, png) | 1 month | Avoid re-downloading large and unchanged assets |
| CSS / JS | 7 days | Optimal for fast updates while still saving bandwidth |
| HTML / PHP | Not cached | Dynamic content, must always be fresh |
immutable header | No cache recheck | The browser will not recheck files that are already cached |
Then restart Apache to save the changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Test the cache that has been set:
[root@localhost ~]# curl -I http://focusnic.biz.id
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Sat, 26 Jul 2025 13:22:44 GMT
Server: Apache
Last-Modified: Fri, 11 Jul 2025 14:56:11 GMT
ETag: "2b-639a882be8970"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 43
Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate
Expires: 0
Pragma: no-cache
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Compression
For compression configurations like mod_deflate and mod_brotli, they should be set server-wide.
The next important thing is compression in Apache using the mod_deflate and mod_brotli modules, which are used to compress content output before sending it to the browser, especially HTML, CSS, JS, XML, and JSON. The main goal is to save bandwidth and speed up loading times.
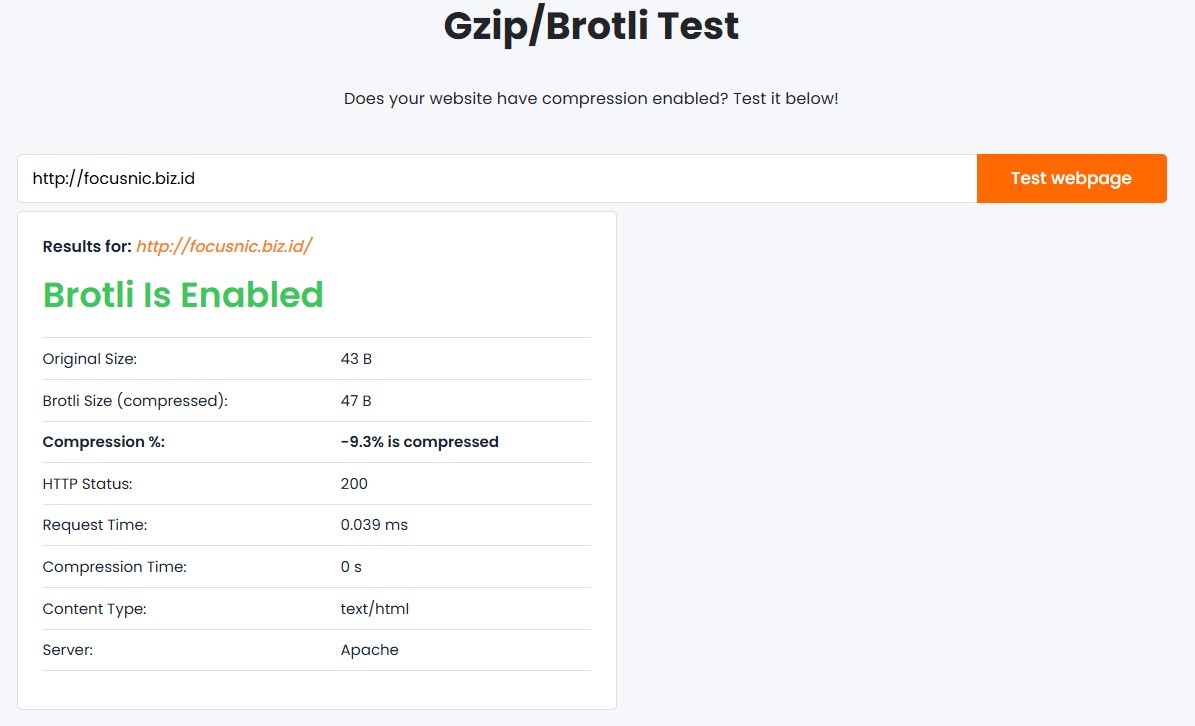
Will enabling mod_deflate and mod_brotli simultaneously cause a conflict? The answer is no. Apache automatically chooses the compression format (br or gzip) based on the browser's Accept-Encoding. Here are the encodings for each module:
- Deflate/Gzip →
Content-Encoding: gzip - Brotli →
Content-Encoding: br
First step, make sure the following modules are active:
httpd -M | grep brotli
httpd -M | grep deflate
Output example:
brotli_module (shared)
deflate_module (shared)
If it doesn't appear or isn't activated, please edit the following configuration:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-base.conf
Add the following parameters:
LoadModule brotli_module modules/mod_brotli.so
LoadModule deflate_module modules/mod_deflate.so
Then restart Apache to save the changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
To enable server-wide compression, please edit the following file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Add the following parameters at the end of the file:
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html text/plain text/css application/javascript application/json application/xml
Header append Vary Accept-Encoding
SetEnvIfNoCase Request_URI \.(?:gif|jpe?g|png|webp|mp4|zip|pdf)$ no-gzip dont-vary
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_brotli.c>
BrotliCompressionQuality 5
AddOutputFilterByType BROTLI_COMPRESS text/html text/plain text/css application/javascript application/json application/xml
Header append Vary Accept-Encoding
SetEnvIfNoCase Request_URI \.(?:gif|jpe?g|png|webp|mp4|zip|pdf)$ no-brotli dont-vary
</IfModule>
Parameter explanation:
-
mod_deflate: This line tells Apache to enable compression using GZIP (DEFLATE) for certain MIME types, namely: html pages, plain text, css, javascript, json, xml. Apache will compress the output of these content types if the browser supports GZIP via the Accept-Encoding header. An exception is made: if the URL request ends with one of the following extensions: .gif, .jpg, .jpeg, .png, .webp, .mp4, .zip, .pdf then Apache will not compress the content. -
mod_brotli: Specifies the quality of Brotli compression, from 1 (fast but large) to 11 (smallest but CPU-heavy). A value of 5 is a compromise between performance and efficiency. -
Header append Vary Accept-Encoding: Tells the proxy/CDN cache that different content can be sent depending on the encoding the browser supports. -
dont-vary: Prevents adding Vary to content.
Then restart Apache to save changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Then try opening a browser and check the browser console or use this site to check the gzip/brotli test https://www.giftofspeed.com/gzip-test/
HTTP/2
HTTP/2 is only active for HTTPS (port 443), it does not run on HTTP (port 80).
HTTP/2 significantly improves performance over HTTP/1.1, especially for modern sites with many assets (images, CSS, JS). HTTP/2 brings many optimization features that improve speed, efficiency, and user experience.
Check the http2 module on Apache:
httpd -M | grep http2
Output example:
http2_module (shared)
If it is not active, please edit the following file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/10-h2.conf
Remove comments (#) or add the following parameters:
LoadModule http2_module modules/mod_http2.so
Restart Apache to save changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Make sure you have a virtual host and SSL, this time I will use an existing virtual host that has SSL Let's Encrypt installed:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id-le-ssl.conf
Add the Protocols h2 http/1.1 parameter inside the <VirtualHost> line:
IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
Protocols h2 http/1.1
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/focusnic.biz.id/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
Kemudian restart Apache untuk menyimpan perubahan:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Conclusion
Tuning and configuring Apache on AlmaLinux 8 is crucial for ensuring maximum stability, efficiency, and performance from your web server. By setting the appropriate MPM, enabling caching, adjusting the number of connections, managing logs, and implementing basic security controls, we can maximize Apache's capabilities for both high traffic loads and complex production scenarios. Optimal Apache configuration isn't just about powering up and running; it should be tailored to your workload, number of users, content types, and modern features like HTTP/2 and compression. The combination of MPM tuning, caching, keepalive, and compression can result in a fast, resource-efficient, and SEO-friendly server.
Q: What is the best MPM to use on AlmaLinux 8?
A: The event MPM is the best choice for high performance, especially for websites with many keep-alive connections.
Q: Can mod_php be used with the event MPM?
A: Not recommended. Use PHP-FPM instead of mod_php for compatibility with the event MPM.
Q: Is it necessary to use a CDN even if you have caching enabled in Apache?
A: A CDN still helps distribute content globally and speeds up access for international users. Local caching and a CDN work in tandem.
Q: Is Apache tuning sufficient, or is kernel tuning also necessary?
A: For maximum performance, kernel tuning, such as sysctl and TCP settings, is also highly recommended, especially for very high traffic.
Q: Can mod_deflate and mod_brotli be used together?
A: Yes. Apache will choose one based on the browser's capabilities (Accept-Encoding). There will be no conflicts, and content will not be compressed twice.
Q: Is KeepAlive server-wide?
A: Yes. Directives like KeepAlive, MaxKeepAliveRequests, and KeepAliveTimeout are server-wide and should be placed in httpd.conf.
Q: How do I prevent compression of already compressed files?
A: Use a directive like the following:
deflate:
SetEnvIfNoCase Request_URI \.(?:gif|jpe?g|png|webp|mp4|zip|pdf)$ no-gzip dont-vary
brotli:
SetEnvIfNoCase Request_URI \.(?:gif|jpe?g|png|webp|mp4|zip|pdf)$ no-brotli dont-vary
Q: What is the formula for calculating MaxRequestWorkers?
A: MaxRequestWorkers = Total RAM / Memory per Apache process
Q: How do I clear the Apache cache?
A: For mod_cache_disk: manually delete the contents of the CacheRoot folder, for example:
rm -rf /var/cache/httpd/mod_cache_disk/
Q: How do I make sure Brotli & Deflate are working?
A: Use curl:
curl -H "Accept-Encoding: br" -I http://focusnic.biz.id
curl -H "Accept-Encoding: gzip" -I http://focusnic.biz.id