Load Status Apache
Managing Apache web server performance in an AlmaLinux 8 environment requires careful monitoring of server workload. One important, often overlooked, yet incredibly useful feature is Apache Load Status. This module allows system administrators and DevOps administrators to monitor real-time server load, active connections, and ongoing HTTP request responses. In this guide, we'll cover in detail how to enable, configure, and optimize Apache mod_status on an AlmaLinux 8 system to ensure peak server performance.
mod_status is a built-in Apache module that allows us to access detailed information about the current server status. The data displayed includes:
- Number of HTTP requests being processed
- Active connections
- Idle workers
- Average request processing time
- Apache CPU load
By enabling Apache Load Status, administrators can perform troubleshooting, make scalability decisions, and monitor system load more precisely.
Prerequisites
- Full
rootaccess - Basic Linux Command Line
- Security
- Apache/HTTPD installed
- Domain (optional)
- Timezone configured
Configure mod_status
Before enabling mod_status, ensure that Apache is installed and running on your AlmaLinux 8 system. If not, please install it with the following command:
dnf update -y
dnf install httpd -y
systemctl enable --now httpd
Also make sure that ports 80 and 443 are open on the firewall:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}
firewall-cmd --reload
By default, the mod_status module is usually included during Apache installation. To verify this, run:
httpd -m | grep status
Output example:
status_module (shared)
If it is not already active, add the following line to the main Apache configuration file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Fill in the following parameters at the very bottom:
LoadModule status_module modules/mod_status.so
Virtualhost for Load Status
Apache Load Status (mod_status) should only be accessed by administrators, not per VirtualHost. mod_status provides the status of the entire Apache instance, not just per-VirtualHost. If customers view /server-status, they can:
- Identify other domains hosted on the shared server
- Determine high and low traffic levels from other domains
- View the URI path being accessed
To be more structured and in line with production practices, add the mod_status configuration in the VirtualHost context, for example:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/status.focusnic.biz.id.conf
Fill in the following parameters:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin admin@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName status.focusnic.biz.id
<Location "/server-status">
SetHandler server-status
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Restricted Access"
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/.htpasswd
Require valid-user
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
Then create a user and password file:
htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/.htpasswd adminstatus
Restart Apache to save changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Access the browser http://$DOMAIN_NAME/server-status and enter the username adminstatus and the password that has been set:
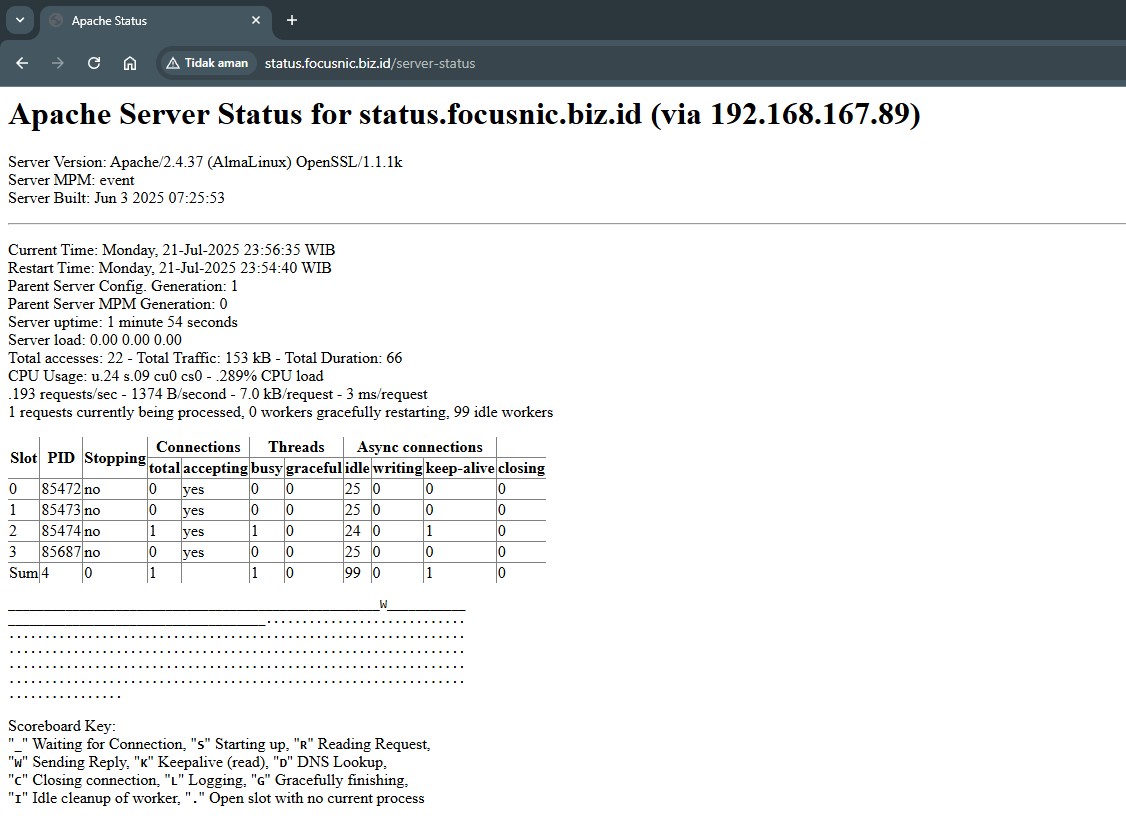
Troubleshooting
If the /server-status page doesn't appear:
- Check Module: Ensure
mod_statusis enabled - Check Firewall: Ensure port 80 is open
- Check Access IP: Ensure your IP is listed in
Require ip - Check Error Log: Check
/var/log/httpd/error_logfor configuration errors
Conclusion
Configuring Apache Load Status on AlmaLinux 8 systems is a crucial step in managing performance and monitoring web server infrastructure in real-time. By understanding and correctly implementing this feature, we can improve efficiency, speed up response times, and prevent downtime due to server overload.
Q: What is Apache Load Status (mod_status)?
A: Apache Load Status is a built-in feature of the Apache HTTP Server, via the mod_status module, that allows administrators to view real-time server status, including the number of active connections, idle workers, and system load.
Q: Is mod_status enabled by default?
A: Not always. In some installations, this module is available but not enabled. You can check this with the command:
httpd -M | grep status
If it is not already active, add LoadModule status_module in the Apache configuration.
Q: How do I access the /server-status page?
A: Once the module is enabled and configured, you can access it via the URL: http://localhost/server-status
Q: Who can access the Load Status page?
A: Only administrators should access this page. Never make this page available to the public or customers, as the data displayed is sensitive and reflects all server activity.
Q: Can mod_status be set per VirtualHost?
A: Functionally, no. mod_status displays the status of the entire Apache server, not just within the context of a single domain or VirtualHost. Therefore, it is not recommended for customers to access it.
Q: Is it safe to enable mod_status on a public server?
A: Not safe if unrestricted. It is highly recommended to:
- Restrict IP access
- Use Basic authentication
- Place status on an internal subdomain
Contoh konfigurasi:
<Location "/server-status">
SetHandler server-status
Require ip 127.0.0.1
</Location>
Q: What if a customer wants to monitor their traffic?
A: Use a more suitable solution such as:
- AWStats or Webalizer
- Dedicated log files per VirtualHost
- Monitoring dashboards such as Grafana with Prometheus that only display their data
Q: Can the /server-status page be used as a monitoring tool?
A: Yes. Many tools like Zabbix, Nagios, and Prometheus can utilize this page for data scraping and notification systems.
Q: Does mod_status cause additional server load?
A: Not significantly. This module is very lightweight because it only reads Apache's internal status. However, frequent access from bots or monitoring tools should be controlled to avoid unnecessary load.
Q: What if the status page doesn't display?
A: Check the following:
- The
mod_statusmodule is active - The configuration is correct
- It's not blocked by the firewall
- Your IP is included in the `Require ip`` list
- There are no configuration errors (see the
/var/log/httpd/error_loglog)
Q: Can you display Apache status via the command line without mod_status?
A: Yes, although it's limited. Use:
apachectl status
Output example:
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/httpd.service.d
└─php-fpm.conf
Active: active (running) since Mon 2025-07-21 23:57:49 WIB; 12min ago
Docs: man:httpd.service(8)
Process: 21228 ExecReload=/usr/sbin/httpd $OPTIONS -k graceful (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 85761 (httpd)
Status: "Total requests: 7; Idle/Busy workers 100/0;Requests/sec: 0.0096; Bytes served/sec: 36 B/sec"
Tasks: 278 (limit: 11143)
Memory: 131.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
├─85761 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─85763 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─85764 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND