Complete Guide on How to Install ownCloud using LAMP Stack on AlmaLinux 8
ownCloud is a popular open-source file sharing and cloud storage platform that allows us to securely store, manage, and share data. By combining the LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP) in AlmaLinux 8, we can build a reliable, secure, and accessible private cloud solution from anywhere.
This guide will cover installing ownCloud using the LAMP Stack on AlmaLinux 8 in a comprehensive, structured, and detailed manner, making it suitable for both personal and corporate use.
Prerequisites
- Full root access
- Domain (optional)
- Basic Linux Command Line
Preparation
Make sure the firewall and SELinux have been adjusted or temporarily disabled if you want to avoid problems during the initial installation.
Before starting the Shopware installation, make sure your AlmaLinux 8 server is up to date and ready to install the LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP).
dnf update -y
dnf install epel-release -y
Install Apache
Apache is a reliable web server and is widely used in production environments. To install it, run the following command:
dnf install httpd -y
Once the installation is complete, enable and start the Apache service with the following command:
systemctl enable --now httpd
To allow access to the server via HTTP and HTTPS, allow the firewall:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}
firewall-cmd --reload
Install PHP
At the time of writing this guide, ownCloud v10 is still running PHP 7.4. Therefore, we will be installing PHP 7.4 even though it has reached EoL. https://central.owncloud.org/t/announcement-owncloud-10-and-php-versions/40251.
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a server-side programming language that is crucial in this stack. We will install PHP 7.4 from the Remi Repository to use the latest version of PHP.
Run the following command to install the Remi Repository:
dnf install -y https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm
Then list the available PHP using the following command:
dnf module list php
Output example:
AlmaLinux 8 - AppStream
Name Stream Profiles Summary
php 7.2 [d] common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php 7.3 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php 7.4 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php 8.0 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php 8.2 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
Remi's Modular repository for Enterprise Linux 8 - x86_64
Name Stream Profiles Summary
php remi-7.2 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php remi-7.3 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php remi-7.4 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php remi-8.0 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php remi-8.1 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php remi-8.2 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php remi-8.3 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
php remi-8.4 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language
Hint: [d]efault, [e]nabled, [x]disabled, [i]nstalled
Enable the desired PHP module version. For example, for PHP 7.4, run the following command:
dnf module reset php -y
dnf module enable php:remi-7.4 -y
Once the repository is active, we can proceed with installing PHP along with the commonly used essential modules:
dnf install -y php php-cli php-common php-mysqlnd php-fpm php-opcache php-gd php-curl php-mbstring php-xml php-json php-soap php-bcmath php-zip php-intl php-posix
Check the installed PHP version with the following command:
php -v
Install MariaDB
MariaDB is a replacement for MySQL and is compatible with MySQL-based applications. Run the following command to install it:
dnf module list mariadb
Output example:
AlmaLinux 8 - AppStream
Name Stream Profiles Summary
mariadb 10.3 [d] client, galera, server [d] MariaDB Module
mariadb 10.5 client, galera, server [d] MariaDB Module
mariadb 10.11 client, galera, server [d] MariaDB Module
Hint: [d]efault, [e]nabled, [x]disabled, [i]nstalled
The output above shows that the default version of MariaDB is 10.11 (the latest version from the OS). However, we'll use MariaDB version 11.4.7 using the official repository at https://mariadb.org/download/ and then reset MariaDB to remove it from the OS's default repository:
dnf module reset mariadb
Run the following command to add the MariaDB version 11.4.7 repository:
nano /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
Add the following parameters:
# MariaDB 11.4 RedHatEnterpriseLinux repository list - created 2025-07-31 14:04 UTC
# https://mariadb.org/download/
[mariadb]
name = MariaDB
# rpm.mariadb.org is a dynamic mirror if your preferred mirror goes offline. See https://mariadb.org/mirrorbits/ for details.
# baseurl = https://rpm.mariadb.org/11.4/rhel/$releasever/$basearch
baseurl = https://mirror.its.dal.ca/mariadb/yum/11.4/rhel/$releasever/$basearch
module_hotfixes = 1
# gpgkey = https://rpm.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgkey = https://mirror.its.dal.ca/mariadb/yum/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck = 1
Then run the following command to install MariaDB:
dnf install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
Enable and activate the MariaDB service:
systemctl enable --now mariadb
systemctl status mariadb
Before using it for production or testing, it is best to secure the MariaDB installation first by running the following command:
mariadb-secure-installation
Then follow the instructions that appear:
- Enter current password for root (enter for none) → [ENTER]
- Switch to unix_socket authentication → Y
- Change the root password? → Y
- Remove anonymous users? → Y
- Disallow root login remotely? Y
- Remove test database and access to it? Y
- Reload privilege tables now? Y
Install ownCloud
Before installing ownCloud, we'll first create a virtual host and database (to store ownCloud content, configuration, and structure). Run the following command to create a virtual host:
Make sure you're using a valid domain (FQDN) and that the DNS A record is pointed to the server IP address used on your server.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/focusnic.biz.id.conf
Fill in the following parameters:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@focusnic.biz.id
ServerName focusnic.biz.id
ServerAlias www.focusnic.biz.id
DocumentRoot /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
<Directory /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html>
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
<IfModule mod_dav.c>
Dav off
</IfModule>
</Directory>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Then create a directory on the virtualhost above:
mkdir -p /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
Restart Apache to save changes:
apachectl configtest
systemctl restart httpd
Create a database by running the following command:
mariadb
Then run the following command to create a database, user, and password:
create database owncloud_db;
create user 'owncloud_user'@'localhost' identified by 'rRPDBeJ5q1L6BZB8';
grant all on owncloud_db.* to 'owncloud_user'@'localhost';
flush privileges;
quit;
Download the ownCloud file and place it in the appropriate directory of the virtualhost:
cd /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html
wget https://download.owncloud.com/server/stable/owncloud-complete-latest.tar.bz2
tar -xf owncloud-complete-latest.tar.bz2
mv owncloud/* .
mv owncloud/.htaccess .
Adjust permissions:
find /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
find /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/focusnic.biz.id
Setup ownCloud via http://$DOMAIN. Create a user for ownCloud administration, and also connect to the database you created earlier.
To increase the security level of your ownCloud installation, it is highly recommended to store the data directory in a separate location from public_html. This way, you can protect sensitive data from unauthorized access via the web.
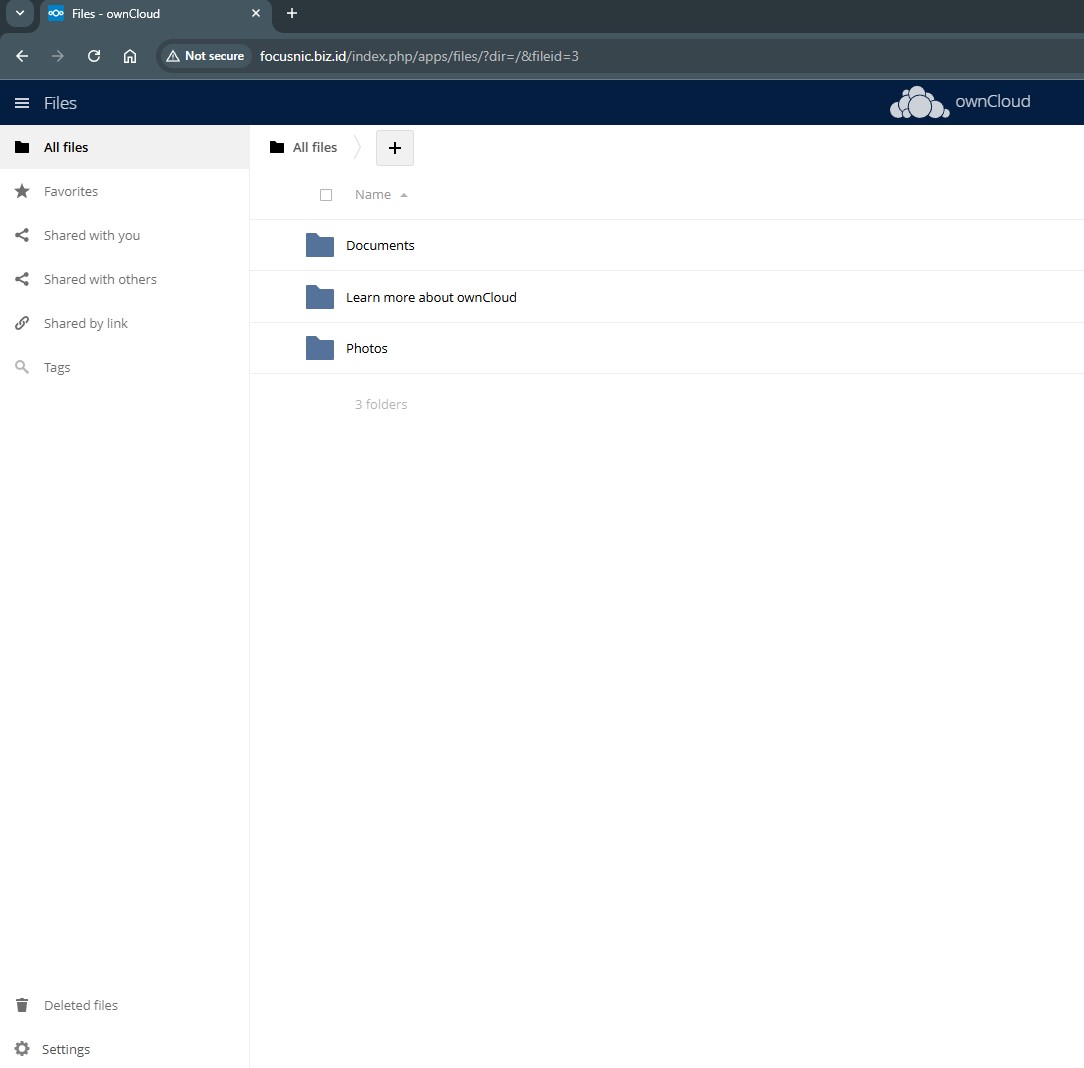
Here is a view of the ownCloud admin dashboard
Troubleshooting
- Error Permission Denied
If a permission denied error appears, ensure the ownCloud folder is owned by the apache user and that permissions are set correctly. Run the following command to set permissions:
find /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
find /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/focusnic.biz.id
- PHP Version Error
Since the ownCloud 10 installation in this guide still uses PHP 7.4, ensure your PHP version matches the one recommended by ownCloud.
- HTTP 500 Error
Check the Apache error log at /var/log/httpd/focusnic.biz.id-error.log.
- Cron Job Not Running
Cron has not been configured or the Apache user does not have access rights. Run the following command:
sudo crontab -u apache -e
Add the following parameters:
*/5 * * * * php -f /var/www/focusnic.biz.id/public_html/cron.php
Conclusion
Using ownCloud on AlmaLinux 8 with a LAMP Stack provides complete control over personal and corporate data. The installation process involves installing Apache, MariaDB, and PHP, as well as manually configuring ownCloud for optimal performance.
For those who don't want the hassle of installing or configuring it yourself, don't hesitate to use Focusnic's services, which provide professional, fast, and secure server and cloud VPS installation services.
Q: Is ownCloud free to use?
A: Yes, ownCloud has a free, open-source community version.
Q: How many PHP versions does ownCloud support?
A: ownCloud supports PHP 7.4 and up to the latest stable version according to the official documentation.
Q: Can ownCloud be accessed from a smartphone?
A: Yes, ownCloud has official mobile apps for Android and iOS.
Q: Can I migrate ownCloud from an old server to a new one?
Yes, by moving the data files and database and then resetting the configuration.
Further References: